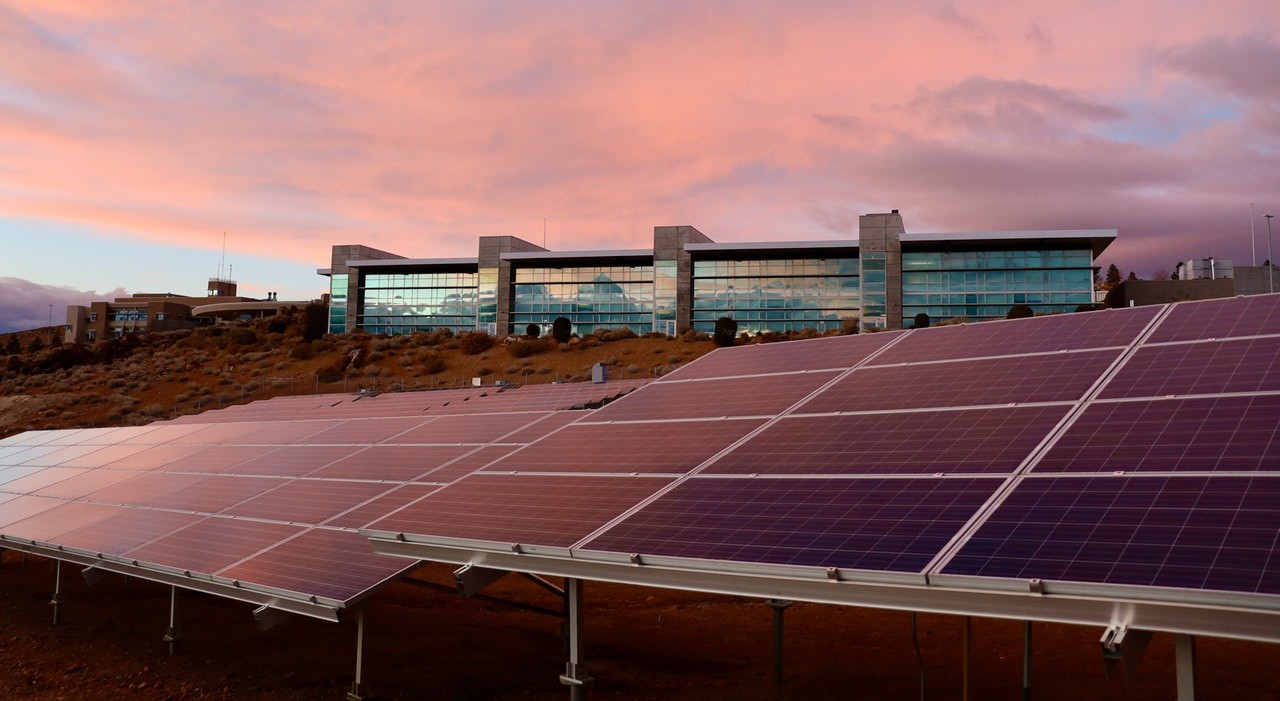
Panasonic will terminate solar panel and module production plants in 2021, terminate related businesses, and withdraw from competition.
As a well-known Japanese company, Panasonic is no stranger to most consumers. Its brands involve household appliances, aviation, office products and other fields. Its products are also very outstanding and are the first choice of many consumers.
Panasonic’s batteries are also very well-known and widely used in mobile phones, computers and other digital products, but their highlight moments are still in cooperation with the popular car company Tesla.
When Tesla was repeatedly hitting a wall for battery supply, Panasonic reached a cooperative relationship with Tesla and became the exclusive supplier since then. As Tesla has become a representative of new energy car companies, Panasonic Battery has also gained a higher reputation globally and has attracted more companies’ attention.
Based on the cooperation on power batteries, Panasonic is also cooperating with Tesla in the field of solar cells and modules. However, on February 26, 2020, Panasonic announced that it would end the cooperative relationship with Tesla’s super Factory No. 2 solar cells in New York in May of the same year, which has brought the cooperation between the two parties to a freezing point in the past ten years.
Intriguingly, the end of the cooperation between the two parties is not because Tesla’s solar cell business is not working, but because the latter’s business is too good.
It is reported that Tesla’s solar roof and home energy wall have been in short supply in North America in the past two years. This was confirmed in Tesla’s 2020 fourth quarter and full-year earnings report just released. Its energy business has set a new record. It has grown from 1.65GWh in 2019 to 3GWh in 2020, an increase of 83% year-on-year.
It can be seen that Tesla’s demand for solar cells is very strong and did not choose Panasonic, which is likely to be the reason for the cost. In fact, Panasonic’s obstruction in its battery business also reflects the decline of the Japanese photovoltaic industry.

Japan prepared for danger in times of peace
After the “oil crisis” of the last century, governments around the world gradually paid attention to renewable energy. Japan, with scarce resources, not only launched cars with leading fuel economy, but also captured the world’s largest auto market, the United States. At the same time, it also uses its own leading technology to make a layout in the field of clean energy, and photovoltaics is one of them.
In 1997, the number of photovoltaic systems installed in Japan reached 360,000 households, and the cumulative installed capacity reached 1,254MW, leading the world. Its photovoltaic products were also exported to all parts of the world at the beginning of the century, making it the best choice for photovoltaic products at that time.
As Japan’s top company, Panasonic entered photovoltaics a little later. In 2009, when Panasonic acquired Sanyo Electric, Fumio Ohtsubo, then president of Panasonic, said: “After our company acquired Sanyo Electric, the group’s business scope has expanded and deepened.” However, Sanyo Electric did not bring Panasonic higher profits, instead dragged down Panasonic’s performance.
To this end, Panasonic packaged and sold other businesses of Sanyo Electric, and also converted Sanyo Electric’s core business into a solar panel business in 2011, and has high hopes for this approach.
In 2010, Toshiro Shirosaka, then chairman of Matsushita Electric (China) Co., Ltd., revealed that after Panasonic’s acquisition of Sanyo Electric, it will give full play to Sanyo’s advantages in the field of solar and lithium batteries, and gradually expand the proportion of green products in sales. By 2018, we will achieve a 30% sales share target, and we plan to put solar cells on the Chinese market as soon as possible.
The year before Toshiro Kisaka made his statement, in 2009, Chinese photovoltaic companies had just been hit hard by the “financial crisis.” The Ministry of Finance and the Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development issued the “Implementation Opinions on Accelerating the Application of Solar Photovoltaic Buildings”, began to implement photovoltaic subsidies, and the photovoltaic market began to break the ice.
Data show that the total installed capacity of photovoltaics in Japan in 2010 has reached 3.6GW, while the cumulative installed capacity of my country in 2011 was only 2.22GW. Therefore, there is no problem with Panasonic’s strategic planning. At that time, there were well-known companies such as Sony and Samsung with the same layout.
What has shocked the world is that while many Japanese and Korean companies are eyeing my country’s photovoltaic market, it is Chinese photovoltaic companies that have grown rapidly and opened up the Japanese market.

Japanese photovoltaic market opportunities
Before 2012, the Japanese photovoltaic market was relatively closed, and users and investors preferred local brands, especially companies that had gained fame at the beginning of the century, such as Panasonic and Kyocera. Moreover, the construction of a large number of nuclear power plants in Japan is very developed, so the proportion of photovoltaic in new energy is not high.
In 2011, the leakage of the Fukushima nuclear power plant in Japan shocked the world and caused a huge power gap. In this context, photovoltaics has become a key industry. The Japanese government took advantage of the trend to introduce the world’s highest subsidy: 42 yen (approximately RMB 2.61)/kWh for systems less than 10kW, and 40 yen (approximately RMB 2.47)/kWh for systems greater than 10kW to stimulate the rapid growth of renewable energy such as photovoltaics development of.
Japan’s photovoltaic industry, which has been developing relatively steadily, has ushered in an outbreak. Not only industrial and commercial users, but investors also use a large number of funds for photovoltaic project construction. Data show that in 2012, Japan’s new photovoltaic installed capacity increased by 100% compared to 2011, reaching 2.5GW, and in 2015 it was as high as 10.5GW, second only to China and the United States.
During this period, high-quality and low-cost Chinese photovoltaic modules have also entered the field of vision of Japanese users. Of course, they were still skeptical at first, and even required Chinese module manufacturers to purchase additional third-party insurance. Under the test of time, China Photovoltaic companies have gradually gained recognition in the Japanese market. So far, Japanese photovoltaic companies are in decline.
According to survey data released by Japan’s Tokei Industry and Commerce Research, since 2015, the number of bankruptcies of Japanese photovoltaic companies has reached a new height and has remained high.
However, as an established company, Panasonic still has good strength. In February 2018, Panasonic developed a solar cell with an efficiency of 24.7%. The result was confirmed by the Japan Institute of Industrial Technology. Panasonic stated that this is the world’s highest efficiency of practical area crystalline silicon solar cells. Compared with the conversion efficiency of leading photovoltaic modules in 2020, this conversion efficiency is also slightly better, which shows the strength of Panasonic in photovoltaic technology.
However, the reason for the decline of most Japanese companies, including Panasonic, is not the backward technology, but the persistence to technology, which makes it difficult to reduce the cost on a large scale in the later stage. This is also the fundamental reason why Panasonic announced to cut down the production of solar cells and modules.

The rise of China’s photovoltaics
According to the person in charge of a Chinese photovoltaic company, even if the import-related costs are included, the price of Chinese photovoltaic modules is still much lower than that of Japanese products, so there is no need to consider the prices of Japanese companies’ products.
It is reported that after exiting solar cell production, Panasonic will use solar cells purchased from other companies to focus on the house energy management business that integrates new energy with storage batteries and control equipment.
It is worth noting that at present, my country’s photovoltaic companies have a strong advantage in the entire industry chain. Whether it is an established Japanese company such as Panasonic or other companies, it is difficult to stop this group advantage.



 2021-02-24
2021-02-24