How you choose to wire your solar panel is actually important, and it affects the performance of your system and the inverter you will be able to use.
What is Solar Panel in Series?
When you connect the MC4 positive terminal of one solar panel to the MC4 negative terminal of the other solar panel, you are creating a series connection. When two or more solar panels are connected like this, it becomes a photovoltaic source circuit.
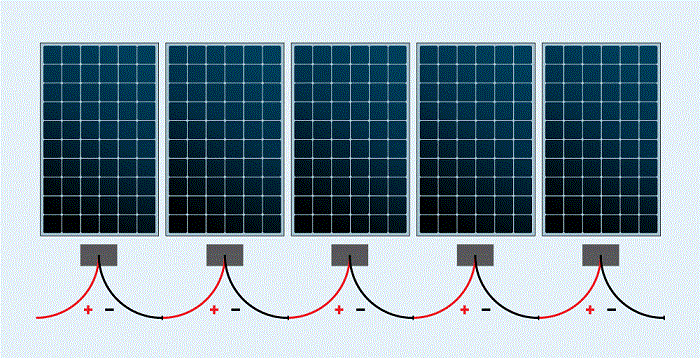
When solar panels are connected in series, the voltage of the solar panels increases, but the current remains the same. It is necessary to increase the voltage of the solar array because the photovoltaic system needs to operate at a certain voltage for the inverter to work properly. Therefore, you can connect solar panels in series to meet the operating voltage window of the inverter.
What is Solar Panels in Parallel?
When the solar panels are connected in parallel, the MC4 positive terminals of the two solar panels are connected together, and the MC4 negative terminals of the two solar panels are connected together. The positive wire is connected to the positive MC4 connector inside the combiner box, and the negative wire is connected to the negative MC4 connector. When multiple solar panels are connected in parallel, it is called a photovoltaic output circuit.
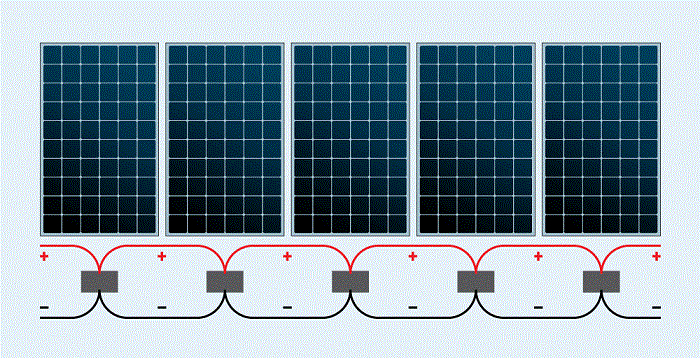
Connecting solar panels in parallel increases the current, but the voltage remains the same. Wiring in parallel allows you to have more solar panels that can generate energy without exceeding the inverter operating voltage limits. The inverter also has a current limit, which you can meet by paralleling the solar panels.
What is the Difference Between Solar Panel in Series and Solar Panel in parallel?
The charge controller is the deciding factor in the wiring of the solar panel. Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) charge controllers are used for solar panels in series, and Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) charge controllers are used for parallel solar panels.
A circuit connected in series works the same way as a solar panel. If one solar panel in a series circuit fails, the entire circuit fails. However, a faulty panel or loose wire in a parallel circuit will not affect the production of the remaining solar panels. How the solar panels are wired depends on the type of inverter used.
In Practical Applications, Choose Series Wiring or Parallel Wiring?
In theory, parallel wiring is a better choice for many electrical applications, because even if one of the solar panels fails, the other panels can function normally. However, it is not always the best choice for all application scenarios. You may also need to meet certain voltage requirements for the inverter to operate.
In order for your solar array to perform at its best, both voltage and amperage need to be considered, achieving a critical balance of voltage and amperage. So, in most cases, solar installers will design a mix of series and parallel connections for your solar array. This allows the system to run at higher voltages and currents without overloading the inverter, so your solar panels can run optimally.



 2024-09-02
2024-09-02