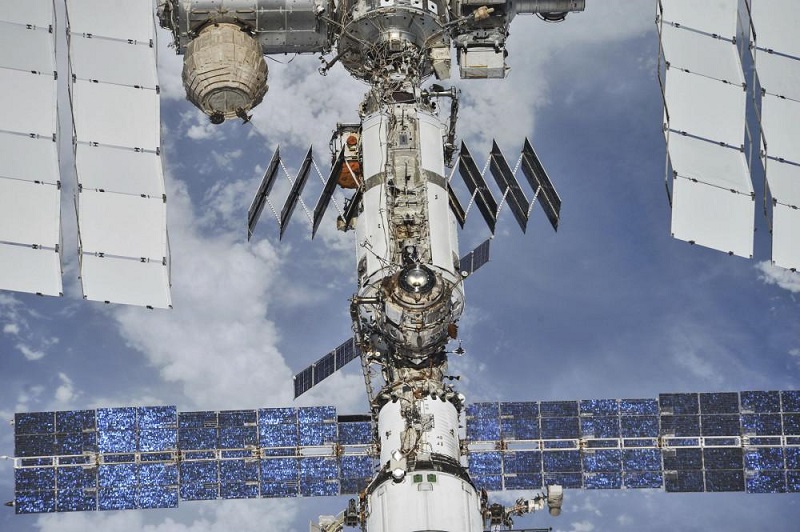
On April 29, the Long March 5B Yao-2 carrier rocket carried the space station Tianhe core module into the air successfully at the Wenchang Space Launch Site in China. This is another historic moment in the history of my country’s manned spaceflight following the complete success of the first flight of the Long March 5B carrier rocket in May 2020.
China Manned Space Station, referred to as China Space Station or Tiangong Space Station, is a space laboratory system with Chinese characteristics assembled in orbit. The orbital height of the space station is 400-450 kilometers, the inclination angle is 42-43 degrees, the manned space station is named “Tiangong”, and the cargo spacecraft is named “Tianzhou”. The China Space Station uses the three-cabin “Tianhe Core Module”, “Wentian Experimental Module” and “Mengtian Experimental Module” as the basic configuration.
The Tianhe core module is the command and control center of the future space station. The daily life of the astronauts will be carried out here, and certain space science experiments and technical experiments will be carried out here. In order to make the long-term life of astronauts in space more comfortable, the core module provides about 50 cubic meters of space for astronauts to work and live. In addition to upgrading the sleeping area, a special sanitation area and a sports area have also been added. In addition, WIFI can be connected to the Internet in the core cabin. With such a huge system, the electricity demand is correspondingly upgraded to nearly three times that of the “Tiangong No. 2″, which requires strong power protection.
In space, the only source of energy for the core module is solar energy. Therefore, the Tianhe core cabin is equipped with two pairs of large-area solar cell wings, with a single wing area of 67 square meters. It converts solar energy into electric energy in the illuminated area for use in the entire cabin, and at the same time stores energy for the battery for use when the core cabin flies to the shaded area. The initial power generation capacity of these two sets of solar cell wings exceeded 18,000 watts, far exceeding any previous spacecraft in China.
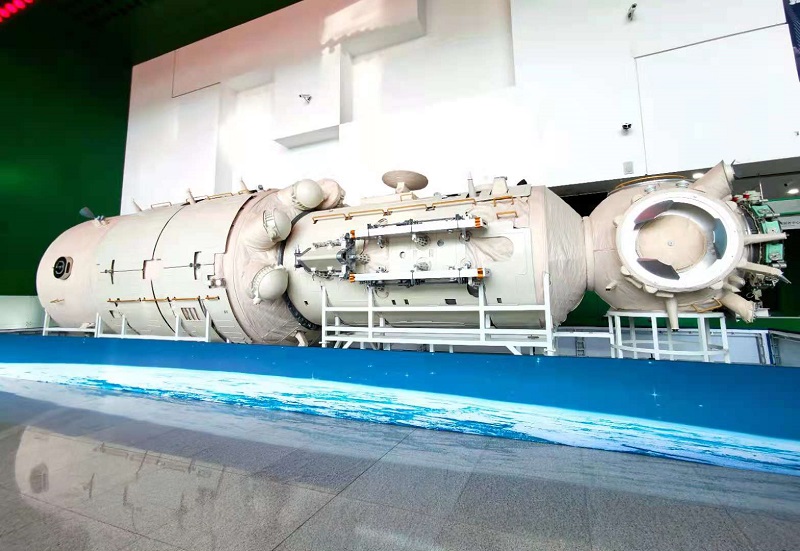
The single-wing span of the solar battery wing of “Tiangong-2″ is only 3 meters, and the single-wing deployment of the battery wing of the Tianhe core cabin has increased to 12.6 meters. The loading space of the launch vehicle is limited, and the developers have applied the flexible solar battery wings of multi-dimensional and multi-step deployment for the first time in China, and this problem has been solved ingeniously. Benefiting from the application of triple-junction gallium arsenide solar cells with high-efficiency photoelectric conversion efficiency, they, together with high-specific energy lithium-ion batteries, form a powerful power system to provide reliable and sufficient uninterrupted power generation for the space station.
Another special function of the core cabin solar battery wing is that the entire wing can be disassembled and transferred during orbit. Taking into account that the solar cell wings of the core cabin will be blocked after the completion of the subsequent space station construction, which will affect power generation, the two solar cell wings can be disassembled and transferred outside the cabin by the astronauts and robotic arms, and installed in the tail of the experimental cabin for subsequent launches. On the truss, the power supply channel is rebuilt on the orbit to realize the function of expanding the energy on the orbit.
The space station has been operating stably for a long time in orbit, and the astronauts stay for a long time. The safety of the station is the most critical issue. When the space station runs into a shadow area where the sun cannot be irradiated, the lithium-ion battery is responsible for powering the entire cabin. How to ensure the safety of the battery?
Researchers have found a solution after long-term research. They designed a long-life, large-capacity, high-safety lithium-ion battery that meets the operational needs of the space station. The battery uses a ceramic diaphragm, which has a good effect of preventing internal short-circuits. At the same time, flame-retardant materials are used in the battery pack to prevent the battery from burning due to high temperatures.
It is reported that there are 6 sets of lithium-ion batteries in the core compartment of the space station, each with 66 single cells. The researchers also designed an intelligent lithium battery management system to achieve high-precision, high-reliability, and high-safety lithium battery charging control. The three-level protection mechanism is activated when the battery is charging, and temperature monitoring is implemented. When the charging temperature is higher than the set safe temperature value, the battery will be charged immediately.
During the space station’s in-orbit operation for more than 10 years, astronauts need to periodically replace lithium batteries in orbit. How to ensure the safe operation of astronauts without affecting the normal power supply of the space station? The developers have provided “double insurance” for the lithium battery replacement operation. The core compartment has two power channels. When one of the channels needs to be replaced with a battery, the other channel is used as the main power supply. In each power channel, when the battery in any unit needs to be replaced, the unit is powered off, and the remaining two units can ensure the normal power supply of this channel.
In addition, the researchers installed two parallel segmented switches in the lithium-ion battery module. By reducing the voltage of the battery pack to the safe voltage range of the human body, it meets the 36-volt safety voltage requirement of the human body and protects the astronauts in the field. Personal safety during rail maintenance.
After the core module is successfully launched, the next mission will be the “Tianzhou II” cargo spacecraft, and then the manned spacecraft will be launched. After the “Tianzhou II” docks with the core module, it will carry three astronauts. The “Shenzhou XII” spacecraft will also enter the launch preparation phase. The launch of the Tianhe core module officially opened the prelude to the construction of China’s space station, and was also an important milestone in the history of China’s manned spaceflight. It marked that the construction of my country’s space station has entered the stage of full implementation and laid a solid foundation for subsequent missions.




 2021-05-03
2021-05-03